How Consumer Values Have Shifted in Covid Pandemic Challenging Brands To Find Their Purpose
Furniture World News Desk on
9/29/2020
For years companies have been looking for ways to contribute in meaningful, measurable ways to society and the environment. That need for corporate purpose beyond just making money has only accelerated since the Covid pandemic hit.
A survey among 1,000 corporate employees conducted by McKinsey back in October 2019 found that 82% said it is important for their companies to have a purpose, but only 42% felt their organization’s purpose statement had any impact.
One wonders if that survey were taken today – after the disruption caused by the coronavirus and the widespread social unrest of the #BlackLivesMatter movement – how much greater the need for purpose would be, as well as how much lower their assessment of their corporation’s impact?
For any consumer-facing business, like a retail or CPG brand, that purpose must align with the consumers’ values.
“Personal values form the stable lens through which a consumer views the world,” explains psychologist Thomas Lacki, Ph.D., senior fellow, research with Resonate, a marketing research intelligence firm that powers B2C marketing.
“Values reflect consumers’ priorities, guide how decisions are made, and motivate actions. Simply put, values encapsulate the ‘why’ behind the ‘buy’ and enable a marketer to connect to the central core of consumers,” he continues.
Consumer values shift, pre- and during the pandemic
A new study from Resonate, “Changes in Consumers’ Personal Values during the Coronavirus Crisis,” details just how much consumer values have shifted pre-Covid and now as we still slog through it. What’s remarkable about the findings in the series of longitudinal surveys among some 2,000 adult Americans is just how much more important specific values have become.
The surveys conducted before and during the pandemic include questions about 19 personal values that are organized into four categories:
- Openness to Change: Pleasure-seeking and looking for excitement, novelty, challenges
- Self-Transcendence: Broadminded and open, accepting different beliefs and behaviors, interested in preserving the environment
- Conservation: Not wanting to “rock the boat,” is polite, tactful, self-disciplined, organized, dependable, fulfills obligations
- Self-Enhancement: Seeks to maintain good public image, social respect, aims to acquire wealth and influence
These values are based upon the Theory of Basic Human Values by professor Shalom H. Schwartz.
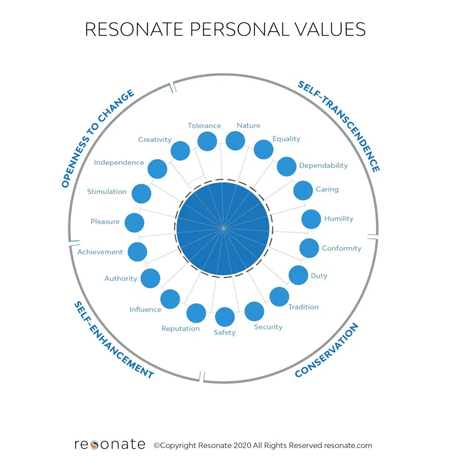 Personal Values Wheel
Personal Values Wheel
Going into the pandemic only seven values were rated as important by a majority of consumers – Dependability (65%), Caring (61%), Safety (57%), Pleasure (55%), Independence (52%), Humility (51%), and Equality (50%).
While in the pandemic, five more values achieved majority status – Security (68%), Tolerance (54%), Nature (52%), Duty (52%), and Creativity (50%).
And the seven pre-pandemic values rated important rose even higher – Caring (75%), Safety and Dependability (both 73%), Independence (63%), Equality (61%), Pleasure and Humility (both 59%).
Even some of the least important values pre-COVID grew in importance during – Conformity (48%), Tradition (44%), Reputation (30%), Stimulation (27%), Achievement (14%), Influence (11%), and Authority (5%).
To make sense of this jumble of data and what it means for consumer-facing brands, I sat down with Lacki and and Ericka McCoy, Resonate’s chief marketing officer.
They are quick to point out that their survey measures human, i.e. consumer, not corporate values, but since companies are made up of humans too, it’s on these values where consumer and corporate purpose intersect.
“Everything starts with humans,” McCoy states. “The best relationships between brands and consumers, just like any other relationship, start with understanding. So if a brand better understands its consumers, it can have a better relationship with them.”
Lacki and McCoy also stress that the values shift seen in the surveys suggests that the “locus of control” for some consumers is moving from internal or personal control to that of external, outside influences. This is consistent during periods of heightened levels of anxiety.
“In a crisis of this nature it encourages consumers to have a heightened awareness and sensitivity to their values. It puts a focus on their inner self during a turbulent time when the world around them is in a state of flux,” Lacki observes.
With people looking to outside influences to help them maintain inner control, it gives brands greater opportunities to guide, direct and influence consumer behavior.
Brands need to better understand their consumers’ values
McCoy cautions that too many brands make broad assumptions about their customers’ values by looking only at their internal data and their customers’ behavior within specific vertical categories of shopping. However, the human dimension of values spans across all consumer categories and purchase behaviors.
“Brands tend to focus on demographic, geographic and psychographic data, but with a values lens, companies can get a much more detailed, micro-segmented look at their audience to tailor experiences and marketing messages very precisely,” she says.
She gives an example of how a major CPG company missed an important customer segment using traditional research methods.
“One of their brands felt they totally understood who their customers were: on-the-go Millennials. Yes, that was one segment of customers, but when we dug into the data, we found there was a whole segment of Baby Boomers who were nostalgic for the brand that they were missing,” she says, and adds, “Too many brands look aspirationally at their segments or who they want their customers to be, rather than actually looking at the data and observing the total picture.”
She shares another faulty assumption about consumer motivations in loyalty programs that miss opportunities that may be more rewarding to a certain segment of customers.
For example, loyalty programs are usually geared to point rewards that members can redeem for savings on future purchases. “However, there are lots of customers who are not point-centric. They would have greater brand loyalty if their points could be translated into a donation to a cause they really care about, like the environment,” she shares.
Using traditional market research methods, brands may be missing important value dimensions that could translate into even greater brand loyalty and affinity.
“Our platform includes 200 million individual profiles of adult Americans with 13,000 attributes for each profile. That allows for micro-segmentation to learn things not just about customers when they are shopping with you, but also what they do when they’re not shopping. It allows an astute marketer to adjust their messaging at the individual level,” she continues as she gives the following examples:
Nike or Under Armour
“On the surface, both Nike and Under Armour customers are athletic and have many things in common, like participating in team sports and exercise classes, belonging to gyms and buying food based on nutrition. But they are very different on specific values,” she explains.
The top personal values for Nike customers are equality, protecting all people and social justice, and tolerance and acceptance of different individuals, beliefs and behaviors. Those are values seen clearly as authentic to the Nike brand, specifically its Colin Kaepernick and women-targeted #DreamCrazy campaigns.
On the other hand, UA shoppers, which skew female, are more traditional, value caring for friends and family and want to maintain traditions, including religious devotion.
Both Nike and Under Armour customers are keen on living a life full of excitement, novelty and challenges, but Nike shoppers are more driven by social and professional status while Under Armour shoppers are driven to gain recognition from their peers.
“Both brands’ audiences want to be the first to know and buy the latest products,” McCoy shares. “And both are active brand engagers who contact companies to share their thoughts, but Nike shoppers are two-times as likely to do so. Further, Nike shoppers are 64% more likely than UA shoppers to shop based on an important issue.”
Columbia or Patagonia
These two brands – Columbia and Patagonia – both target outdoor enthusiasts who value stimulation and excitement. But that is where the similarities end.
Columbia shoppers are driven by authority, to be in charge, direct the activities of others, and to take risks to gain rewards. They also value creativity and seek freedom to think up new ideas and develop new skills. Life for them is about exploration and learning new things and being imaginative.
For Patagonia shoppers, authority doesn’t even make their list. Rather than wanting to be perceived as an authority, Patagonia customers are more self-reliant, and likely to seek solutions to problems themselves rather than depend on others. They desire freedom to determine their own actions. They are also keen on nature and protecting and preserving the natural environment.
These different values translate into distinctively different marketing messages for the brands. Columbia communicates authority through product-centric advertising. Patagonia’s voice is based on value-centric messaging which translates into Patagonia shoppers being 56% more likely to shop based on an important issue.
Chicken or Egg?
In closing our discussion, I asked whether the values of a brand’s customers determine the brand’s values and purpose or if the brand’s values determines the customers it attracts. “Our research shows that a brand can’t just adopt a set of values just because they want to adopt a set of values,” McCoy says. “A brand has to be authentic in their values.”
She goes on to share that the recent wide-spread adoption of the #BlackLivesMatter cause may seemed inauthentic to a group of customers. She cautions brands not to jump on the band wagon for what seems like a worthy cause because it might distance more customers than it attracts, especially if it doesn’t ring true to other values the brand upholds.
“We found about 20% of our audience said they would shop more with a brand that supports #BlackLivesMatter, but then 30% of the audience said they would shop less,” she reports.
Ultimately, the purpose and values of a brand must align with the values of their customers. Which comes first isn’t the real question, rather it is the need for brand values to evolve with that of their customers.
While the 19 core values that Resonate captures are cross-culturally stable over time, how consumers reflect them in their shopping behavior may change, as they have done in the face of the Covid crisis.
Understanding consumer values gives brands new ways of forging deeper relationships with customers that will pay off in greater customer loyalty and help grow customer lifetime value. And by aligning with their customers’ values, brands will have customers who are more likely to forgive mistakes, willing to pay a higher price and to promote the brand to their friends and family.
When corporate purpose aligns with customer’s values it is win/win for both.
About Pam Danziger: Pamela N. Danziger is an internationally recognized expert specializing in consumer insights for marketers targeting the affluent consumer segment. She is president of Unity Marketing, a boutique marketing consulting firm she founded in 1992 where she leads with research to provide brands with actionable insights into the minds of their most profitable customers.
She is also a founding partner in Retail Rescue, a firm that provides retailers with advice, mentoring and support in Marketing, Management, Merchandising, Operations, Service and Selling.
A prolific writer, she is the author of eight books including Shops that POP! 7 Steps to Extraordinary Retail Success, written about and for independent retailers. She is a contributor to The Robin Report and Forbes.com. Pam is frequently called on to share new insights with audiences and business leaders all over the world. Contact her at pam@unitymarketingonline.com.